March
2017
HYDROCARBON
ENGINEERING
44
Fluid catalytic cracking pre-treat
The pre-treatment of feed for fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) units
offers significant performance advantages for FCC operation
including overall increase in conversion, improved yield
selectivity, FCC products that meet clean fuels specifications,
and reduced catalyst usage. Many refiners have leveraged the
advantages offered by fluid catalytic cracking pre-treat (FCCPT)
units to increase profitability and flexibility. In light of the critical
role that this technology plays in modern refining, Criterion has
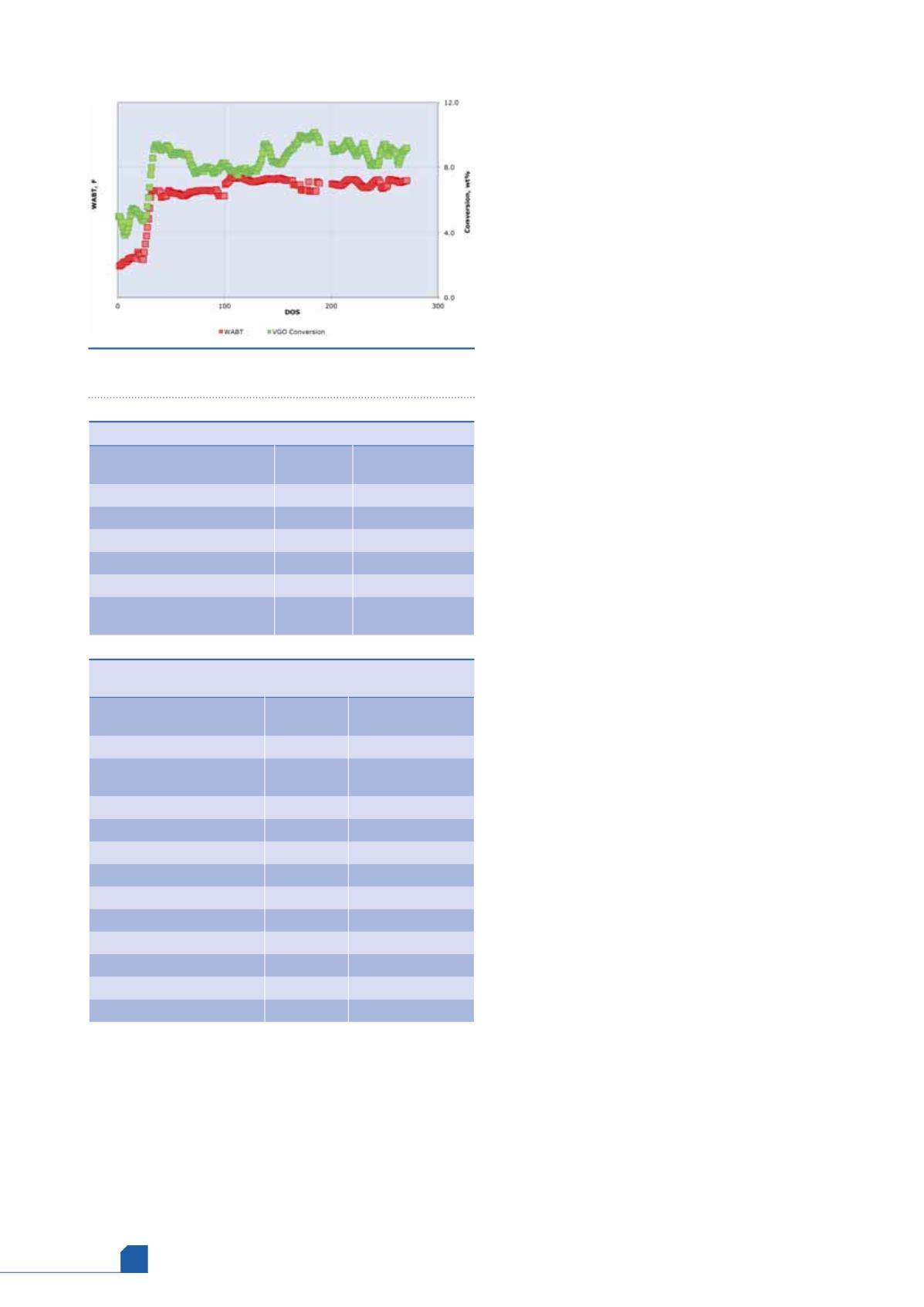
Figure 3.
Impact of FCCPT severity on vacuum gasoil (VGO)
conversion.
Table 3.
CENTERA FCCPT performance in Tier 3 mode
FCCPT performance
Typical
Criterion
Tier 3 mode
Operating mode
HDS
Arosat
TLP volume gain (LV% of feed)
Base
+ 1.25
Product sulfur (ppmw)
1000
300
Product nitrogen (ppmw)
500
100
API gain (°)
Base
+ 1.2
Distillate conversion (wt% of
feed)
Base
+ 4.1
Table 4.
Impact of improved FCCPT performance on
FCC
FCC
Typical
Criterion Tier 3
mode
Combined feed sulfur (ppmw)
1200
570
Combined feed nitrogen
(ppmw)
360
160
Combined feed API (°)
Base
+ 0.7
Riser top (°F)
Base
- 20
Conversion (%)
Base
+ 0.5
Gasoline sulfur (ppmw)
46
10
Gasoline octane (R+M/2)
Base
Base
Dry gas (wt% of feed)
Base
- 0.51
TLP volume gain (LV% of feed) Base
3.9
Gasoline (LV% of feed)
Base
+ 3.66
LCO (LV% of feed)
Base
+ 0.27
Slurry make (LV% of feed)
Base
- 0.35
continued to develop and apply new advanced
catalysts and solutions for FCCPT applications.
CENTERA catalysts have demonstrated excellent
hydrogenation performance, as well as effective HDS
and HDN activity. A key feature of these products is
their synergistic behaviour when applied in stacked
systems.
The saturation of aromatics enables improved
product upgrade for increased FCC yields while also
increasing the rate of deep desulfurisation via direct
desulfurisation routes. In addition, the high
hydrogenation activity enables increased HDN, both
improving FCC feed quality as well as improving
hydrotreater performance as nitrogen inhibits the HDS
reaction. The hydrogenation of FCC feed streams is
necessary for deep desulfurisation especially when
operating at a higher HDS target for Tier 3 FCC gasoline
production. As such, many refiners have included the
application of high severity FCCPT operation in their
strategies for Tier 3 fuels production since FCC gasoline
is a major blend component of the mogas pool. As
discussed previously, the synergy offered by the
strategic application of NiMo and CoMo catalysts
greatly improves the hydrogenation horsepower of the
overall catalyst system. This is in contrast to the
performance of single catalyst systems, which require
the promotion from Ni on a CoMo catalyst to perform
enhanced HDS.
Example one
The following commercial example illustrates the
performance achieved by a refiner operating an FCCPT
unit to produce a Tier 3 quality gasoline blend
component, increasing conversion in the FCCPT unit as
well as conversion and yields on the FCC unit. This unit
is currently operating with CENTERA technology in a
stacked catalyst system at targeted operating
conditions for maximum performance. Figure 3, Table 3
and Table 4 highlight the performance benefits achieved
post application of Criterion’s technology compared to
a typical catalyst system. The technology has resulted
in an increase in FCCPT conversion and FCC
performance with improved yields, while the catalyst
system remains on target to provide an extended life
cycle.
Example two
The run length (Figure 4) of this high pressure FCCPT
unit was increased from 18 to 36 months by
implementing a stacked system using CENTERA NiMo
DN-3651 and CoMo DC-2650 and an improved
OptiTrap
TM
grading design. These two improvements
resolved both activity loss and chronic delta P (dP)
growth in the unit. The catalyst system delivered better
than expected improvements in activity; SOR
temperature was on target and stability was also
improved. In beds one and two, which needed to be
skimmed halfway through the cycle, dP increased
rapidly. A number of changes were made to the grading
scheme in the top beds (loading filter tray cartridges








